Codeforces Round 895 (Div. 3)
A. Two Vessels
题目翻译
你有两个装有水的容器。第一个容器含有克水,第二个容器含有克水。这两艘船都非常大,可以容纳任意数量的水。
您还有一个空杯子,最多可容纳克水。
一次,您可以从任何容器中舀出多克水,然后将其倒入另一个容器中。请注意,一次倒入的水的质量不必是整数。
使容器中水的质量相等所需的最少移动次数是多少?请注意,您无法执行除所描述的移动之外的任何操作。
思路
每次可以使得两个杯子的差距最多减少2*c,因此答案就是,向上取整
因为c++的/默认是下取整
向上取整可以写成:
或者使用ceil取整
或者使用 a/b+a%b!=0
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:A. Two Vessels
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
int res = (abs(a - b) + 2 * c - 1) / (2 * c);
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
B. The Corridor or There and Back Again
题目翻译
你正处在一条向右无限延伸的走廊里,分成了几个方形的房间。您从房间开始,前往房间,然后返回房间。您可以选择的值。移动到相邻的房间需要秒。
另外,走廊里还有个陷阱:第个陷阱位于房间,将在你进入房间**后秒被激活。一旦陷阱被激活,你就无法进入或离开有该陷阱的房间。
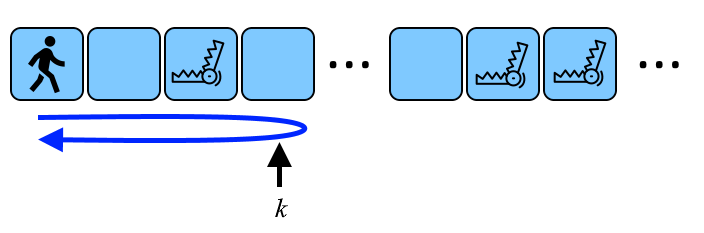
可能的走廊以及通往房间和返回的路径的示意图。
确定的最大值,允许您从房间移动到房间,然后安全返回房间。
例如,如果和,你可以前往房间并安全返回(陷阱在时刻激活,不能阻止你返回)。但如果你试图到达房间,陷阱就会在时刻激活,阻止你返回(你会在第二个返回的路上尝试进入房间,但激活的陷阱会阻止你)。 任何更大的值也是不可行的。故答案为。
思路
因为数据范围比较小,可以直接暴力枚举时间1-300,看是否合法,取合法的最大时间
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:B. The Corridor or There and Back Again
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, int>> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1, x, y; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = {x, y};
}
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 300; i++) {
bool ok = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if ((i - a[j].first) * 2 >= a[j].second) {
ok = 0;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
mx = max(mx, i);
}
}
cout << mx << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
C. Non-coprime Split
题目翻译
给你两个整数。你需要找到正整数和,使得同时满足以下条件:
或报告它们不存在。
表示数字和的【最大公约数】(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greatest_common_divisor)。例如、、。
思路
如果l=r,那么就看l是不是素数,如果是素数就无解,否则可以找到一个因子x,另一个数为l-x,而,因此
如果l!=r:
- r为奇数,此时r-1>=l ,并且r-1一定为偶数,因此可以构造 (2,r-1-2), 他们的gcd=2;
- r为偶数,可以直接构造(2,r-2),gcd=2;
此外,还需要特判一些误解的情况。
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:C. Non-coprime Split
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
//13 14 15 16 17
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
void solve() {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
if (l == 1 && r <= 3) {
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
if (l == 2 && r <= 3) {
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
if (l != r) {
if (r & 1) {
cout << 2 << " " << r - 1 - 2 << endl;
} else {
cout << 2 << " " << r - 2 << endl;
}
} else {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= l; i++) {
if (l % i == 0) {
cout << i << " " << l - i << endl;
return;
}
}
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
D. Plus Minus Permutation
题目翻译
给你个整数——、、。我们将排列的分数 称为以下值:
换句话说,排列的得分是所有指数能被整除的之和,减去所有指数能被整除的之和。
你需要在长度的所有排列中找到最大可能的分数。
例如,如果、、,则通过排列获得最高分数,并且等于。
长度的排列是由个从到的不同整数以任意顺序组成的数组。例如,是排列,但不是排列(数字在数组中出现两次),也不是排列(,但数组包含) 】)。
思路
看n里面有几个x的倍数,有几个y的倍数,有几个lcm(x,y)的倍数,
答案应该是x倍数上面的数-y倍数上面的数,lcm(x,y)上面的数不记录答案,因为是一个减去一个加回来
设
我们应该贪心的把x倍数上面的数从大到小放,把y倍数上面的数从小到大放。
n范围比较大,可以使用等差数列求和公式计算。
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:D. Plus Minus Permutation
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int lcm(int a, int b) {
return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}
void solve() {
int n, x, y;
cin >> n >> x >> y;
int t = lcm(x, y);
int x1 = n / x - n / t;
int y1 = n / y - n / t;
int res = 0;
res += x1 * (n + n - x1 + 1) / 2;
res -= y1 * (1 + y1) / 2;
cout << res << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
E. Data Structures Fan
题目翻译
给你一个整数数组,以及一个由个字符组成的二进制字符串 。
Augustin 是数据结构的忠实粉丝。因此,他要求你实现一个可以回答查询的数据结构。有两种类型的查询:
- “1 ”()— 将中的每个字符替换为其相反字符。即,将全部替换为,将全部替换为。
- "2 " () — 计算所有索引的数字的按位异或 的值】 这样。请注意,空数集的被认为等于。
请帮助奥古斯丁回答所有问题!
例如,如果、、,请考虑以下一系列查询:
1.“2”——我们对索引感兴趣,其中,从开始,这些是索引和,所以查询的答案将是。
2.“1 ”——我们需要将字符替换为其反义词,因此在查询之前,在查询之后:。
3.“2”——我们对索引感兴趣,其中,从开始,这些是索引,和,所以答案为查询结果为。
4.“1 ”— 。
5. “2”—,没有带有的索引,因此由于空数集的被认为等于,所以该查询的答案是。
二进制字符串是只包含字符或的字符串。
思路
异或的性质:
- x^x=0
可以使用两个变量zero,one 来记录整个字符串中1上面权值异或的答案,0上面权值异或的答案。
- 对于1操作:
- 将整个字符串翻转,那么对于zero来说,他应该先去掉这个区间中0上权值的异或和(设为
x),再异或上这个区间中1上权值的异或和(设为y), 去掉x可以使用zero^x,因为zero=x^t(其中t为除去这个区间的其他0上权值异或和),这样zero^x=t^x^x=t,再异或上y可以使用zero^y,因此总的操作其实就是zero^x^y=zero^sum,其中sum为这个区间所有权值的异或和
- 将整个字符串翻转,那么对于zero来说,他应该先去掉这个区间中0上权值的异或和(设为
- 对于2操作,直接输出对应的1和0即可。
快速求区间的异或可以使用类似于前缀和思想。
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:E. Data Structures Fan
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
string s;
cin >> s;
s = " " + s;
cin >> q;
vector<int> s1(n + 1);
int x = 0, y = 0; //x-0 y-1
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
s1[i] = s1[i - 1] ^ a[i];
if (s[i] == '1') {
y ^= a[i];
} else {
x ^= a[i];
}
}
while (q--) {
int op, l, r;
cin >> op;
if (op == 2) {
cin >> l;
if (l == 0) {
cout << x << " ";
} else {
cout << y << " ";
}
} else {
cin >> l >> r;
x ^= s1[r] ^ s1[l - 1];
y ^= s1[r] ^ s1[l - 1];
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int q;
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
F. Selling a Menagerie
题目翻译
您是一个动物园的主人,该动物园由只动物组成,编号从到。然而,维护动物园的费用相当昂贵,所以你决定卖掉它!
众所周知,每种动物都害怕另一种动物。更准确地说,动物害怕动物()。另外,每只动物的成本是已知的,对于动物来说,它等于。
您将按固定顺序出售所有动物。正式来说,你需要选择一些排列 ,先卖动物,然后卖动物,依此类推,最后卖动物。
当你出售动物时,有两种可能的结果:
- 如果动物在动物之前**被出售,您将因出售动物而收到钱。
- 如果动物在动物之前未出售,您将因出售动物而收到钱。 (令人惊讶的是,目前害怕的动物更有价值)。
您的任务是选择出售动物的顺序,以使总利润最大化。
例如,如果、,并且您选择的排列是,则:
- 第一个被出售的动物是动物。动物之前没有被出售过,所以你会因为出售它而收到钱。
- 第二个出售的动物是动物。动物之前已被出售,因此您可以通过出售它获得的钱。
- 第三个出售的动物是动物。动物之前没有出售过,所以出售它你会收到钱。
- 第四个出售的动物是动物。动物之前没有出售过,所以出售它你会收到钱。
- 第五个出售的动物是动物。动物之前已被出售,因此您可以通过出售它获得的钱。
通过这种排列选择,您的总利润是。请注意,在本例中,不是最大可能利润。
长度的排列是由个从到的不同整数以任意顺序组成的数组。例如,是一个排列,但不是一个排列(在数组中出现了两次),也不是一个排列(,但出现在数组中)大批)。
思路
根据输入数据,可以从i向a[i]连一条单向边,w[i]为点权,此时可以发现先拿i就可以获得两倍的贡献。因此可以记录每个点的入度,然后按照拓扑排序的方式,先拿入度为0的点,这些点拿了贡献就是两倍,
拿完之后剩下的就是一些环了,环与环之间不会相连,因为一个点最多有一个出边。
对于一个环,显然需要拿出一个点,这个点的代价为1倍,这样其他点点代价可以做到两倍,因此只需要找到这个环里面权值最低点哪个点,最后拿这个点,就可以做到贡献最大化。
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:F. Selling a Menagerie
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> w(n + 1), a(n + 1), d(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
d[a[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> w[i];
queue<int> q;
vector<bool> st(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (d[i] == 0) q.push(i);
}
vector<int> res;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
st[x] = true;
res.push_back(x);
if (--d[a[x]] == 0) q.push(a[x]);
}
//剩下的都是环了
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (st[i])continue;
int x = i;
vector<int> t;
while (!st[x]) {
st[x] = true;
t.push_back(x);
x = a[x];
}
int pos = 0; //权值最小的点的位置
for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j++) {
if (w[t[j]] < w[t[pos]]) pos = j;
}
for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j++) {
pos++;
if (pos == t.size())pos = 0;
res.push_back(t[pos]);
}
}
for (const auto &item: res) {
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
G. Replace With Product
题目翻译
给定一个数组,其中个正整数。您需要恰好执行一次以下操作:
- 选择个整数和(),并将子数组替换为单个元素:子数组中所有元素的乘积。
例如,如果对数组进行参数的运算,则数组将变为。
您的任务是在应用此操作后最大化数组的总和。找到应用此操作的最佳子数组。
思路
显然,如果区间的两边都是1,这些1一定不会选。
可以先找到区间[l,r],区间l的左边都是1,区间r的右边都是1,l和r都不等于1
对于一个区间来说,如果这个区间中元素的乘积大于1e9了,那么我们就会选择将整个区间进行合并,因为对于端点都是>=2的数,显然乘上这些数获得的贡献远比加上这些数获得的贡献大。
如果区间的乘积<1e9,那么说明不会有超过30个数大于1,因此可以记录这些>1的数的位置,然后暴力枚举两个数进行合并,看哪种方案获得的贡献最大,此时不会爆int。
代码
/**
* PROBLEM_NAME:G. Replace With Product
* ONLINE_JUDGE_NAME:Codeforces
* Date:2023/9/7
* Author:houyunfei
**/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES" << endl;
#define no cout << "NO" << endl;
#define IOS cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#define cxk 1
#define debug(s, x) if (cxk) cout << "#debug:(" << s << ")=" << x << endl;
using namespace std;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
int l = 1, r = n;
while (l <= n && a[l] == 1) l++;
while (r >= 1 && a[r] == 1) r--;
if (l >= r) {
cout << "1 1\n";
return;
}
int mul = 1;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
mul *= a[i];
if (mul > 1e9) {
cout << l << " " << r << endl;
return;
}
}
int t = 0;
vector<int> pos;
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
if (a[i] > 1) {
t++;
pos.push_back(i);
}
}
if (t >= 30) {
cout << l << " " << r << endl;
return;
}
vector<int> s(n + 1), sum(n + 1);
s[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
s[i] = s[i - 1] * a[i];
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
}
int x = l, y = l;
int mx = sum[n];
for (int i = 0; i < pos.size(); i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < pos.size(); j++) {
t = s[pos[j]] / s[pos[i] - 1] + sum[n] - (sum[pos[j]] - sum[pos[i] - 1]);
if (t > mx) mx = t, x = pos[i], y = pos[j];
}
}
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
}
signed main() {
IOS
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
